

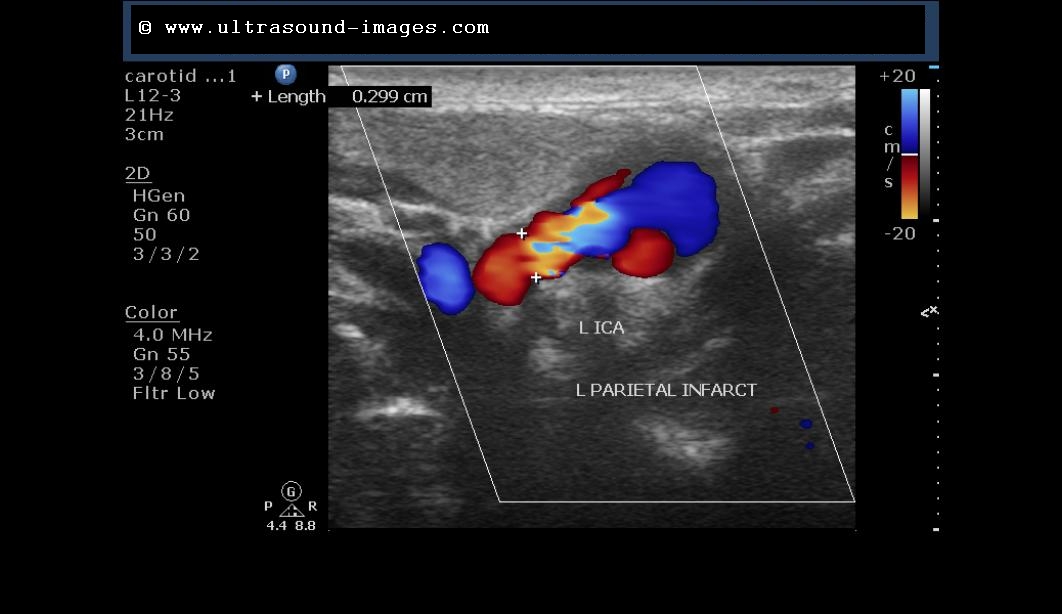
A longitudinal view of the common carotid artery was acquired over which Doppler evaluation of the middle third of common carotid artery were set with the sample volume in the centre of the vessel. Doppler were acquired using Xario 200 Toshiba Diagnostic ultrasound, Japan Made, 7–11 MHz linear transducer in supine position with extended neck. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects, according to the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki, revised in 2000, Edinburgh.
NORMAL CAROTID DOPPLER PEAK SYSTOLIC VELOCITY SERIES
We therefore analyzed the PSV, EDV and resistive index (RI) of the normal common carotid arteries (CCA) to find out if they vary with variable DR.ĪIM: to study the variations of PSV, EDV and RI in the normal CCA with variations in DR expressed in DB.Ī series of 24 consecutive bilateral normal common carotid arteries having normal arterial Doppler waveforms from 12 cases were analysed in the department of Radiology and Imaging, North Eastern Indira Gandhi Regional Institute of Health and Medical Sciences, Shillong, Meghalaya, India. The effect of DR variation on the Doppler parameters in carotid arteries has not been explored till date. While variation of dynamic ranges (DR) can be used for enhancing resolution of sonographic images, exact velocity readings in a disease carotid artery is important for predicting the degree of stenosis. On the other hand increase in peak systolic velocity (PSV) and end diastolic velocity (EDV) above a certain level can predict degree of stenosis in the internal carotid artery with high percentage of sensitivity and specificity on colour duplex ultrasound. In medical ultrasound imaging, dynamic range (DR) is defined as the difference between the maximum and minimum values of the displayed signal to display and it is one of the most essential parameters that determine its image quality, 2 DR is expressed in decibels (dB), higher the dynamic range means more shades of grey and lower dynamic range means more contrast to the images. 1 Therefore Doppler frequency shift is directly proportional to the velocity of target assuming that the transmitted sound and speed of sound in tissues is constant. Ultrasound equipment calculates the velocity of blood flow according to the Doppler equation ΔF=(FR-FT) = 2.FT.V.Cos Ө/c where ΔF- is the Doppler frequency shift, FR – the frequency of sound reflected from the moving target, FT-the frequency of sound emitted from the transducer, V- velocity of the target towards the transducer, C- velocity of sound in the medium, Ө – angle between the axis of flow and the incident ultrasound beam. Open Access This is an open access article distributed under the CC BY-NC license. Copyright © 2018 Association for Research into Arterial Structure and Physiology. Summarised mean value for all PSV of both sides shows significant difference between variable dynamic ranges as determined by One-Way repeated measures ANOVA and Post-hoc analysis revealed that there was a significant difference only between 35 dB to 55 dB and 85 dB.Ĭonclusion: Variable DR while improving sonographic contrast result in significant variation of PSV in the CCA particularly on the right CCA. There was however no significant differences in the PSV of the left CCA EDV and RI at variable dynamic ranges in both the right and left CCA. Results: For PSV of the right CCA at 9 MHz, there was significant differences on variable DR as determined by One-Way repeated measures ANOVA. p value significant at <0.05.Īim: To study the effect of variable dynamic ranges (DR) on the PSV, end diastolic velocity (EDV) and resistive index (RI) of CCA.
Statistical analysis: One-Way repeated measures ANOVA parameters expressed as Mean ± SEM. PSV, EDV and RI at 9 MHz transducer frequencies and variable DR of 35,45,55,65,75 &85 Decibels (dB) were compared. Materials and methods: Normal Doppler waveforms of 24 CCA from 12 healthy individuals of age 22–28 years were analysed in the department of radiology, NEIGRIHMS, Shillong. Peak systolic velocity (PSV) is the best Doppler parameter for quantifying carotid artery degree of stenosis. Introduction: Doppler ultrasound is the commonest diagnostic tool used to evaluate the internal, external and common carotid arteries (CCA).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
